Choosing the right Node.js Framework: Express, Koa, or Hapi?
Node.js was first introduced 10 years ago, and in that period of time, has become the fastest-growing open source project on Earth, with +59,000 stars on GitHub and more than a billion downloads.
Part of the reason for the rapid growth in popularity was that Node.js allows developers use the same language for both the client-side and the server-side part of an application: JavaScript.
Node.js is an open-source and cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment designed for building scalable server-side network applications, and it’s a popular tool for almost any kind of project! Because of its exponential growth and popularity, many frameworks were created to enhance productivity, scalability, the speed of applications, to facilitate quick prototyping, and to automate processes with the help of libraries, templates, and reusable components.
In this article, we will explore the differences between three of the most popular frameworks in Node.js: Express, Koa, and Hapi. In a future post, we will look into Next, Nuxt and Nest.
- The comparison is based on:
- Popularity (GitHub Stars and npm downloads).
- Installation.
- Basic Hello World app.
- Advantages.
- Disadvantages.
- Performance.
- Security.
- Community involvement.
Express
Express is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications, it behaves like a middleware to help manage servers and routes.
Installation
For installing express, you need to have already installed Node.js. If you want to install express in a specific directory and save it in the dependencies list:
$ npm install express --save
However, if you want to install Express temporarily and not add it to the dependencies list, you can use:
$ npm install express --no-save
Hello World
This is the most basic example on how to create an express app that listens on port 3000 and responds “Hello World!”:
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.get('/', (req, res) => res.send('Hello World!'))
app.listen(port, () => console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}!`))
For every other path, the server will respond with 404 Not Found.
Advantages
- Almost the standard for Node.js web middleware.
- Simple, minimalistic, flexible and scalable.
- Fast app development.
- Fully customizable.
- Low learning curve.
- Easy integration of third-party services and middleware.
- Majorly focused on browsers, making templating and rendering an almost out of the box feature.
Disadvantages
Although Express.js is a very convenient and easy-to-use framework, it has some minor drawbacks that may influence the development process.
- Organization needs to be very clear to avoid problems when maintaining the code.
- As your codebase size increases, refactoring becomes very challenging.
- A lot of manual labor is required, since you need to create all endpoints.
Performance
Express provides a thin layer of fundamental web application features, without obscuring Node.js features that are familiar.
The best practices for improving express performance includes:
- Use gzip compression.
- Don’t use synchronous functions.
- Do logging correctly (for debugging, use a special module like debug, for app activity use winston or bunyan).
- Handle exceptions properly, using try-catch or promises.
- Ensure your app automatically restarts by using a process manager or use an
initsystem like systemd or upstart. - Run your app in a cluster. You can increase the performance of a Node.js app greatly by launching a cluster of processes (a cluster runs multiple instances of the app, distributing the load and tasks among the instances).
- Cache request results, so that your app does not repeat the operation to serve the same request repeatedly.
- Use a load balancer to run multiple instances of it and distribute the traffic, like Nginx or HAProxy.
- Use a reverse proxy that performs supporting operations on the requests. It can handle error pages, compression, caching, serving files, and load balancing among other things.
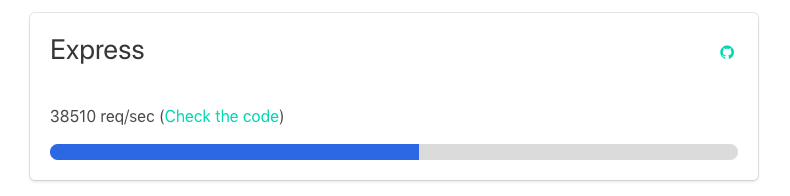
A simple “Hello World” app has the following performance request per second:
Security
You can find a list of security updates in Express in the following link. Node.js vulnerabilities directly affect Express, so is important to keep an eye on Node.js vulnerabilities and make sure you are using the latest stable version of Node.js.
Community involvement
The Express community meets regularly, and they communicate through their mailing list, Gitter, IRC channel, issues in GitHub, and the Express Wiki.
Finally, express is probably the most popular framework for Node.js, and there are many other popular frameworks that are built on Express.
Koa
Koa was built by the same team behind Express, and aims to be a smaller, more expressive, and more robust foundation for web applications and APIs. By leveraging async functions, Koa allows you to ditch callbacks and significantly increase error-handling. Koa does not bundle any middleware within its core, and it provides an elegant suite of methods that make writing servers fast and enjoyable.
A Koa application is an object containing an array of middleware functions which are composed and executed in a stack-like manner upon request.
Installation
Koa requires node v7.6.0 or higher for ES2015 and async function support. You need to have already installed Node.js.
You can quickly install a supported version of node.js with your favorite version manager:
$ nvm install 7
$ npm i koa
$ node my-koa-app.js
Hello World
This is the most basic example of a “Hello World!” app on Koa that listens on the port 3000.
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
});
app.listen(3000);
For every other path, the server will respond with 404 Not Found.
Advantages
- Koa improves interoperability, robustness, and makes writing middleware much more enjoyable.
- Has a large number of helpful methods but maintains a small footprint, as no middleware are bundled.
- Koa is very lightweight, with just 550 lines of code.
- Has a very good user experience.
- Better error handling through try/catch.
- Generated-based control flow.
- No more callbacks, facilitating an upstream and downstream flow of control.
- Cleaner, more readable async code.
Disadvantages
- The open source community around Koa is relatively small.
- Not compatible with Express-style middleware.
- Koa uses generators which are not compatible with any other type of Node.js framework middleware.
Performance
With Koa.js you can build web apps with great performance. This is because you can stop using callbacks, deal with errors faster, and because Koa itself is a very lightweight framework. As well as that, it makes the code management process easier.
It’s important to take into account the best practices for having a better performance in Node.js like running things in parallel, use asynchronous APIs in your code, keeping code small and light, and using gzip compression.
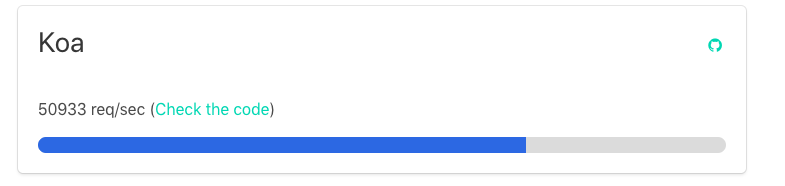
A simple “Hello World” app has the following performance request per second:
Security
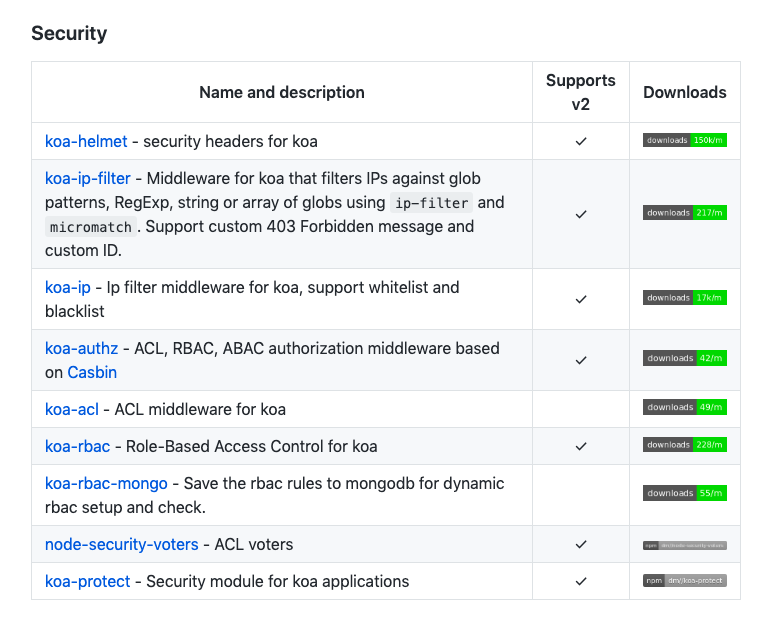
There are different middlewares and headers for Koa that helps to improve the security, you can find them in the following link
Community involvement
You can join G+ koa Community, mailing list, contribute to Koa’s repo, join koa slack or start a discussion in hashnode.
Hapi
Hapi is a rich framework for building applications and services. It enables developers to focus on writing reusable application logic instead of spending time building infrastructure.
It is a configuration-driven pattern, traditionally modeled to control web server operations. A unique feature Hapi has is the ability to create a server on a specific IP, with features like the onPreHandler, we can do something with a request before it is completed by intercepting it and doing some pre-processing on the request.
Installation
To install hapi, you need to have Node.js installed and then:
npm install hapi
To save it to your package.json dependencies.
Hello World
The following example is the most basic hello world app using hapi:
'use strict';
const Hapi=require('hapi');
// Create a server with a host and port
const server=Hapi.server({
host:'localhost',
port:8000
});
// Add the route
server.route({
method:'GET',
path:'/hello',
handler:function(request,h) {
return'hello world';
}
});
// Start the server
const start = async function() {
try {
await server.start();
}
catch (err) {
console.log(err);
process.exit(1);
}
console.log('Server running at:', server.info.uri);
};
start();
Then you just launch the application by running npm start and open localhost:8000/hello in your browser.
Advantages
- It provides a robust plugin system that allows you to add new features and fix bugs at a fast pace.
- It enables you to build scalable APIs.
- There is a deeper control over request handling.
- It is an excellent choice for building Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs because it provides you with routing, input, output validation, and caching.
- You can build an API that serves all kinds of clients that need mobile and single-page applications.
- Detailed API reference and good support for document generation.
- You can use hapi.js with any front-end framework, like React, Angular, and Vue.js to create a single-page application.
- Configuration-based approach to some sub-middlewares(pseudo-middlewares)
- Provides the availability of caching, authentication, and input validation.
- Has a plugin-based architecture for scaling.
- Provides really good enterprise plugins such as joi, yar, catbox, boom, tv, and travelogue.
Disadvantages
- Developers need to figure out the code structure on their own.
- “Locks” developers into using hapi-specific modules and plugins such as catbox, joi, boom, tv, good, travelogue, and yar; and which are not compatible with Express/Connect.
- Endpoints are created manually and must be tested manually.
- Refactoring is manual.
Performance
A 2017 study on Node.js frameworks, showed that hapi performed the worst compared to the other frameworks.
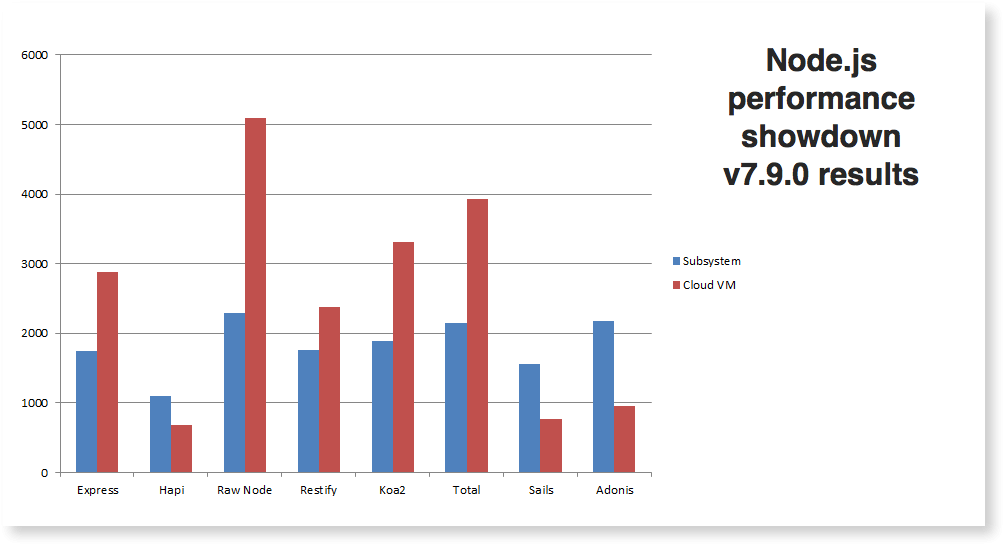
As we can see in the following graph compared to express. This test is consistent with past results. Express continues to maintain a performance edge over hapi. Applications with significant performance requirements should consider the advantage Express has over Hapi.
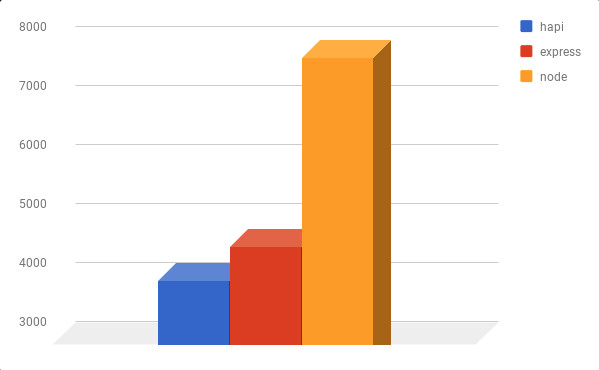
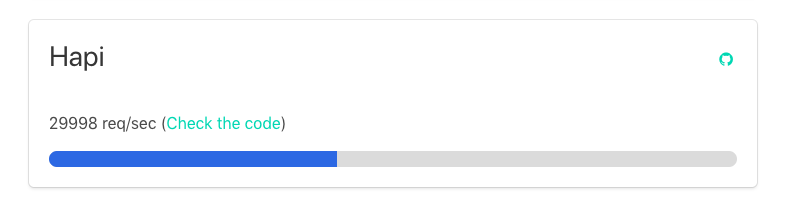
A simple “Hello World” app has the following performance request per second:
Security
Different plugins can help to improve hapi security:
Crumb: Anti cross-site-request-forgery (XCSRF) token generation and validation plugin. It works both with regular requests and CORS requests (OWASP recommends using CSRF protection, such as Crumb, along with CORS). Synopsys recommends using Crumb v3.0.0 or newer since a CSRF token leakage issue has been fixed when using Crumb with CORS enabled and the request origin does not match those specified in the CORS configuration.
Joi: Object schema description language and validator for JavaScript objects. Joi allows developers to define a schema for an object and then evaluate the object against that schema thus performing input validation for the object. Everything is defined and evaluated on the server-side so that the attacker cannot easily bypass this protection.
Hapi-rbac: Allows developers to implement role-based access controls easily. Broad enough to grant or deny access to entire groups; granular enough to grant or deny access to individual users.
Blankie: Allows developers to set the Content-Security-Policy header directives easily. The CSP is flexible enough that it may be implemented on a per route basis or across all routes.
Cryptiles: Provides general purpose cryptographic utilities for random number generation, encryption, hashing and fixed-time comparisons of hashes that are based on the Node.js crypto library.
Community involvement
You can join slack channel: hapihour.slack.com, visit the community page, community governance page and follow them on twitter to keep updated with the latest news.